Conventional lithium-ion batteries based on inorganic cathode materials containing transition metals (e.g., Co and Ni) are facing the ceiling of energy density and the concern of resource sustainability. Therefore, it is necessary to develop novel, highly efficient electrode materials, and rechargeable battery technologies without the limitation of resources.
Organic electrode materials (OEMs), primarily comprised of naturally abundant elements such as C, H, O, N, and S, have attracted increasing attention in recent years due to their numerous advantages, including structural diversity and designability, high theoretical capacity (up to 600 mAh g−1) and energy density (up to 1,000 Wh kg−1), as well as potential cost-effectiveness.
Moreover, the redox reactions of electroactive organic groups have wide compatibility with embedded cations or anions, so OEMs are almost applicable in all kinds of rechargeable batteries, including nonaqueous Li/Na/K/Mg batteries, aqueous Zn batteries, dual-ion batteries, and redox flow batteries. based on structural features, OEMs can be mainly categorized into small molecules, polymers, and metal-organic frameworks (MOFs).
Among them, small-molecule organic electrode materials (SMOEMs) possess much higher material availability and potential on energy density. However, they also suffer from severe dissolution problems and the subsequent shuttle effect in nonaqueous electrolytes, resulting in inferior cycling stability and Coulombic efficiency.
Recently, the group headed by Prof. Zhiping Song from Wuhan University systematically summarized the fundamental knowledge and insights about SMOEMs based on their nearly two decades of experience in the research of OEMs.
In this review, the authors first introduced the cell configurations and working principles of four types of rechargeable batteries based on OEMs, including metal-organic batteries, metal-ion batteries with organic cathodes or anodes, and dual-ion batteries. Subsequently, the reported n-type and p-type electroactive organic groups and units, as well as their redox mechanisms, were clearly categorized.
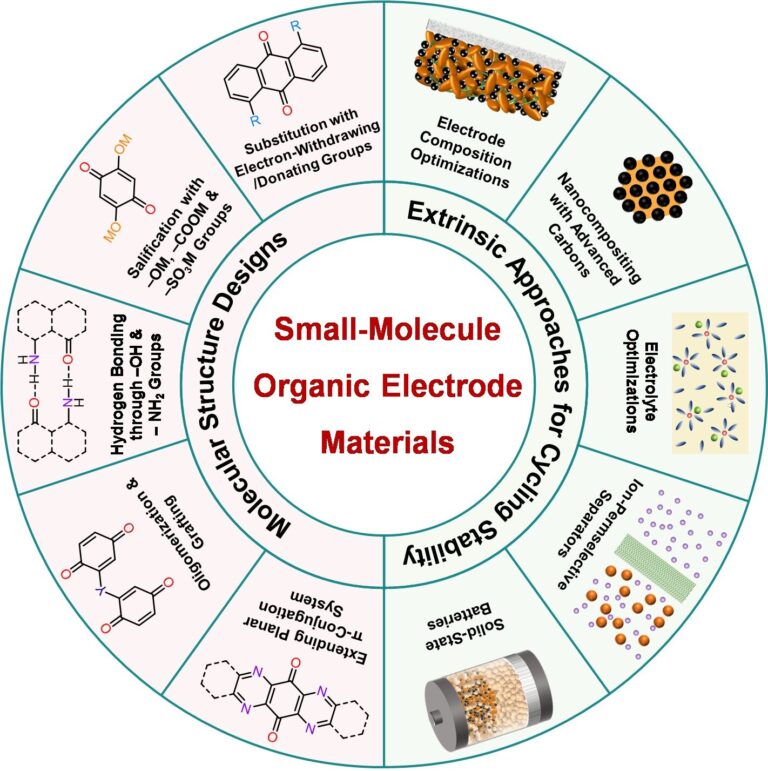
Based on this, they itemized n-type and p-type SMOEMs in detail, illustrated representative examples, and discussed their advantages, disadvantages, and development prospects. Furthermore, aiming at the key challenge of SMOEMs, i.e., the dissolution problem, the authors systematically summarized the main strategies for improving cycling stability from two aspects: molecular structure design methods and extrinsic optimization approaches.
Finally, they put forward their own opinions on the research status and trends of SMOEMs, aiming to guide their development in a more scientific and practical way.
The research is published in the journal Science China Chemistry.
More information:
Xiaotang Gan et al, Small-molecule organic electrode materials for rechargeable batteries, Science China Chemistry (2023). DOI: 10.1007/s11426-023-1738-3
Science China Press
Read the full article here